========
FairML: Auditing Black-Box Predictive Models
FairML is a python toolbox auditing the machine learning models for bias.
Description
Predictive models are increasingly been deployed for the purpose of determining access to services such as credit, insurance, and employment. Despite societal gains in efficiency and productivity through deployment of these models, potential systemic flaws have not been fully addressed, particularly the potential for unintentional discrimination. This discrimination could be on the basis of race, gender, religion, sexual orientation, or other characteristics. This project addresses the question: how can an analyst determine the relative significance of the inputs to a black-box predictive model in order to assess the model’s fairness (or discriminatory extent)?
We present FairML, an end-to-end toolbox for auditing predictive models by quantifying the relative significance of the model’s inputs. FairML leverages model compression and four input ranking algorithms to quantify a model’s relative predictive dependence on its inputs. The relative significance of the inputs to a predictive model can then be used to assess the fairness (or discriminatory extent) of such a model. With FairML, analysts can more easily audit cumbersome predictive models that are difficult to interpret.s of black-box algorithms and corresponding input data.
Installation
You can pip install this package, via github - i.e. this repo - using the following commands:
pip install https://github.com/adebayoj/fairml/archive/master.zip
or you can clone the repository doing:
git clone https://github.com/adebayoj/fairml.git
sudo python setup.py install
Methodology
Code Demo
Now we show how to use the fairml python package to audit a black-box model.
"""
First we import modules for model building and data
processing.
"""
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
"""
Now, we import the two key methods from fairml.
audit_model takes:
- (required) black-box function, which is the model to be audited
- (required) sample_data to be perturbed for querying the function. This has to be a pandas dataframe with no missing data.
- other optional parameters that control the mechanics of the auditing process, for example:
- number_of_runs : number of iterations to perform
- interactions : flag to enable checking model dependence on interactions.
audit_model returns an overloaded dictionary where keys are the column names of input pandas dataframe and values are lists containing model dependence on that particular feature. These lists of size number_of_runs.
"""
from fairml import audit_model
from fairml import plot_generic_dependence_dictionary
Above, we provide a quick explanation of the key fairml functionality. Now we move into building an example model that we'd like to audit.
# read in the propublica data to be used for our analysis.
propublica_data = pd.read_csv(
filepath_or_buffer="./doc/example_notebooks/"
"propublica_data_for_fairml.csv")
# create feature and design matrix for model building.
compas_rating = propublica_data.score_factor.values
propublica_data = propublica_data.drop("score_factor", 1)
# this is just for demonstration, any classifier or regressor
# can be used here. fairml only requires a predict function
# to diagnose a black-box model.
# we fit a quick and dirty logistic regression sklearn
# model here.
clf = LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', C=0.01)
clf.fit(propublica_data.values, compas_rating)
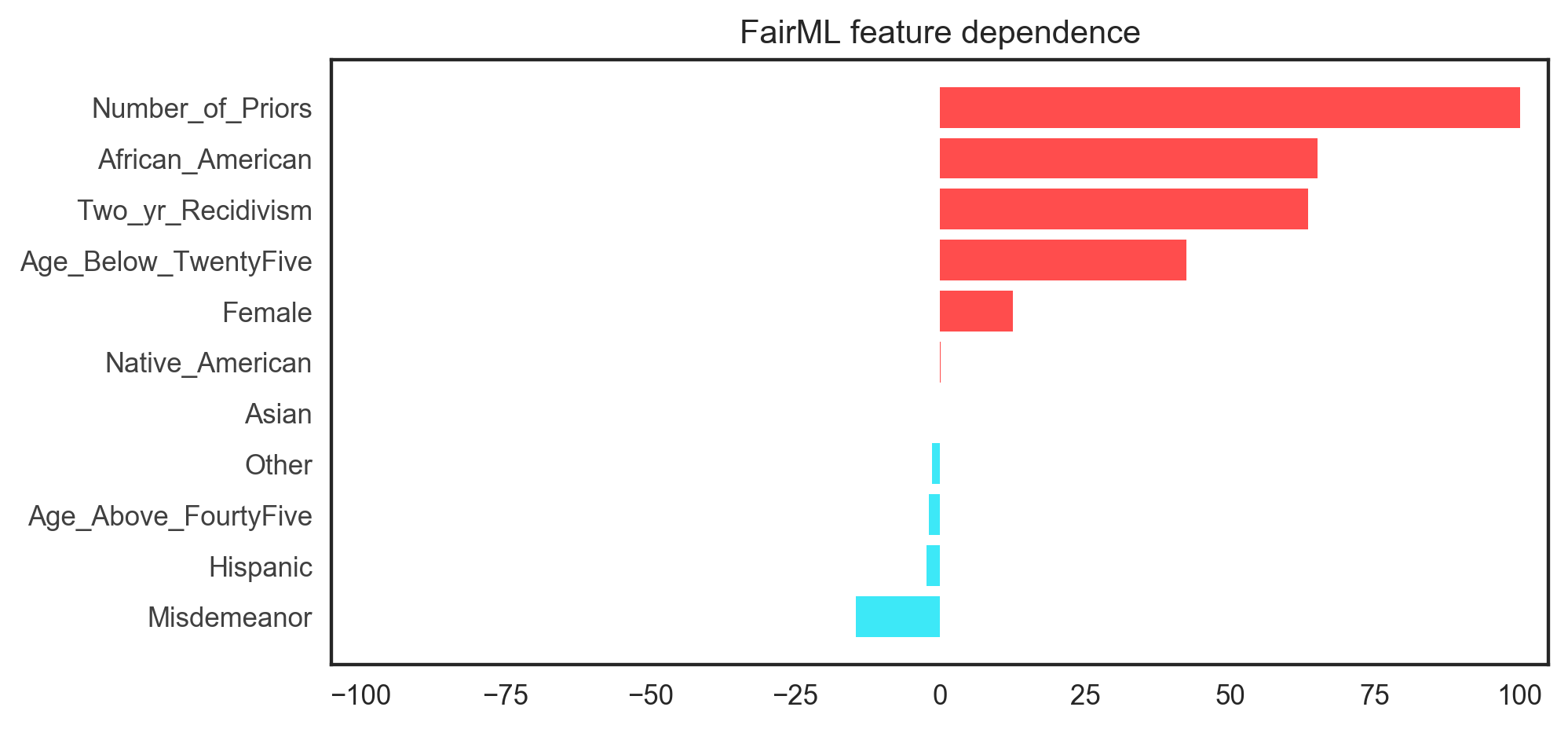
Now let's audit the model built with FairML.
# call audit model with model
total, _ = audit_model(clf.predict, propublica_data)
# print feature importance
print(total)
# generate feature dependence plot
fig = plot_dependencies(
total.get_compress_dictionary_into_key_median(),
reverse_values=False,
title="FairML feature dependence"
)
plt.savefig("fairml_ldp.eps", transparent=False, bbox_inches='tight')
The demo above produces the figure below.
Feel free to email the authors with any questions:
Julius Adebayo ([email protected])
Data
The data used for the demo above is available in the repo at: /doc/example_notebooks/propublica_data_for_fairml.csv